
Askar Akimzhanov, PhD
- Associate Professor
Areas of Interest
Research Interests
Protein S-Acylation, Cell Signaling, Calcium Regulation, Cancer, Immunity
Dynamic Lipidation of Proteins
Protein S-acylation is a reversible post-translational modification of cysteine residues by a variety of fatty acid species. Although protein S-acylation was discovered more than 30 years ago and S-acylated proteins have been implicated in pathogenesis of several diseases including cancer, cardiovascular and immune disorders, it remains one of the most understudied post-translational protein modifications. High lability, one of the key features of protein S-acylation, along with its prominent effect on the protein function, makes it an attractive mechanism for the regulation of intracellular signaling. In particular, rapid changes in the protein palmitoylation (S-acylation with a palmitic acid moiety) status could provide a molecular basis for activation of plasma membrane-localized signaling proteins by targeting them into specific plasma membrane subdomains.
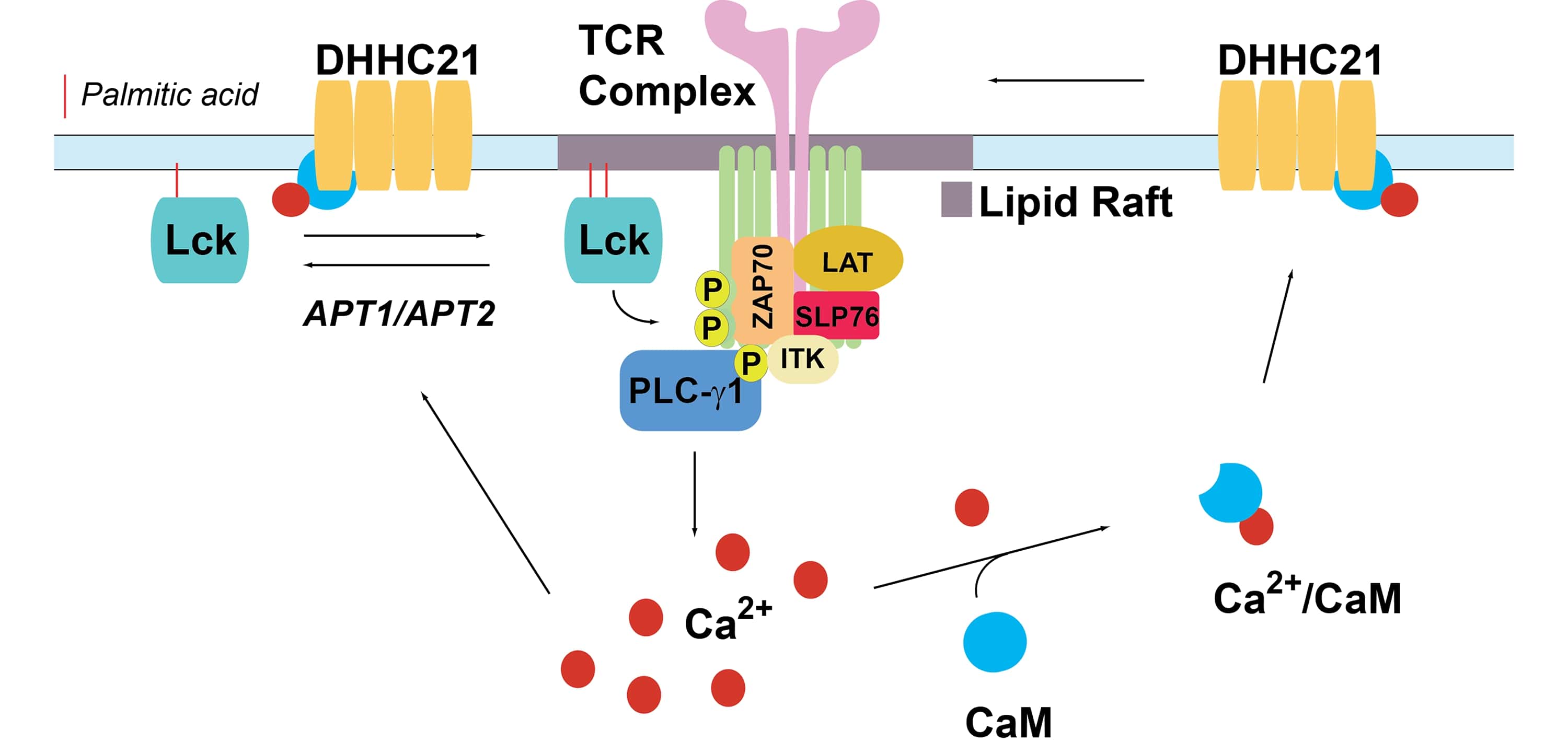
The role of DHHC-mediated protein S-Acylation in regulation of the T-Cell Receptor signaling pathway
We propose a model in which the engaged TCR complex recruits and activates plasma membrane-associated PATs to increase palmitoylation of key signaling proteins. We aim our studies (a) to analyze the dynamics and regulation of stimulus-dependent palmitoylation of Lck, LAT and other members of TCR signaling pathway and (b) to uncover a previously uncharacterized role of DHHC PATs in the regulation of T cell signaling. We expect that inclusion of a novel class of regulatory enzymes into the canonical TCR signaling pathway would greatly expand the range of potential therapeutic targets for diseases associated with altered T cell homeostasis.
Selected Publications
Akimzhanov AM, Boehning D. 2015. Rapid and transient palmitoylation of the tyrosine kinase Lck mediates Fas signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 112(38):11876-80.
Akimzhanov AM, Barral JM, Boehning D. 2013. Caspase 3 Cleavage of the Inositol 1,4,5-Trisphosphate Receptor Does Not Contribute to Apoptotic Calcium Release. Cell Calcium. 53(2):152-8.
Akimzhanov AM, Wang X, Sun J, Boehning D. 2010. T-cell receptor complex is essential for Fas signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107(34):15105-10.
Akimzhanov A, Krenacs L, Schlegel T, Klein-Hessling S, Bagdi E, Stelkovics E, Kondo E, Chuvpilo S, Wilke P, Avots A, Gattenlohner S, Muller-Hermelink HK, Palmetshofer A, Serfling E. 2008. Epigenetic changes and suppression of the nuclear factor of activated T cell 1 (NFATC1) promoter in human lymphomas with defects in immunoreceptor signaling. Am J Pathol. 172(1):215-24.
Akimzhanov AM, Yang XO, Dong C. 2007. Chromatin remodeling of interleukin-17 (IL-17)-IL-17F cytokine gene locus during inflammatory helper T cell differentiation. J Biol Chem. 282(9):5969-72.
Education and Training
PhD
University of Wurzburg, Germany
Postdoctoral Fellow
MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston TX
Postdoctoral Fellow
University of Texas Medical Branch, Galveston TX
Graduate Program Affiliations
Molecular and Translational Biology
Immunology