Areas of Interest
Research Interests
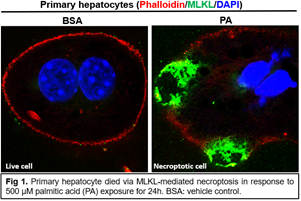
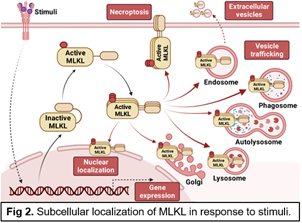
The research program in my lab focuses on 1) understanding the molecular mechanisms for regulating intracellular and extracellular vesicle trafficking and cell death in both metabolic homeostasis and disease; 2) identifying novel therapeutic targets and biomarkers for obesity and fatty liver diseases; 3) repurposing existing drugs for metabolic disease. Given the strong association of the protein mixed lineage kinase domain like pseudokinase (MLKL) with the regulation of cell death (canonical, Fig 1) and membrane trafficking (non-canonical, Fig 2), the current focus is specifically on exploring the canonical and non-canonical roles of MLKL in physiological and pathophysiological conditions. The lab will also leverage basic biological insights to develop new preventative approaches and therapeutic strategies for the treatment of metabolic disease.
The lab uses genetically engineered mice and a broad spectrum of techniques such as confocal imaging, intravital imaging, flow cytometry, RNA-sequencing, and proteomics techniques and bioinformatics approaches paired with targeted mechanistic strategies to explore the basis and functional consequences of dysregulated homeostatic signaling from both patients and mouse models.
Publications
- Wu XQ, Fan XD, McMullen MR, Miyata T, Kim A, Pathak V, Wu JG, Day, L, Hardesty J, Welch N, Dasarathy J, Allende DS, McCullough AJ, Jacobs JM, Rotroff DM, Dasarathy S, Nagy L. (2023). Macrophage-derived MLKL in alcohol-associated liver disease: regulation of phagocytosis. Hepatology, 77:902-919.
- Feng XS, Xuan RR, Dong YC, Wu XQ, Cheng YP, Yuan ZN, Dong H, Han JM, Zhong F, Zhao JJ, Fan XD. (2023). Changes in Clinical Manifestations Due to AFLD Retyping Based on the New MAFLD Criteria: An Observational Study Based on the National Inpatient Sample Database. Diagnostics (Basel). 13(3):488.
- Wu JG, Kim A, Wu XQ, Ray S, Allende DS, Welch N, Bellar A, Dasarathy J, Dasarathy S, Nagy L. (2023). 5S rRNA pseudogene transcripts are associated with interferon production and inflammatory responses in alcohol-associated hepatitis. Hepatology, 77:1983-1997.
- Wu XQ, Fan XD, Miyata T, Kim A, Cagigas-Du Ross CK, Ray S, Huang E, Taiwo M, Arya R, Wu JG, Nagy L. (2023). Recent advances in understanding of pathogenesis of alcohol-associated liver disease. Annu Rev Pathol, 18:411-438.
- Fan XD*, Fang JS*, Wu XQ*, Poulsen K, Miyata T, Kim A, Yu L, Wang XY, Zhang X, Han QY, Liu ZW. (2021). Effect of HIV infection on pre- and post-liver transplantmortality in patients with organ failure. (*Co-first author), HIV medicine. 22(8):662-673.
- Poulsen KL, Fan XD, Kibler CD, Huang E, Wu XQ, McMullen MR, Leng L, Bucala R, Ventura-Cots M, Argemi J, Bataller R, Nagy LE. (2021). Role of MIF in coordinated expression of hepatic chemokines in patients with alcohol-associated hepatitis. JCI Insight. 1414206(11):e141420.
- Kim A, Wu XQ, Allende DS, Nagy LE. (2021). Gene deconvolution reveals aberrant liver regeneration and immune cell infiltration in alcohol-associated hepatitis. Hepatology. 74(2):987-1002
- Miyata T*, Wu XQ*, Fan X, Huang E, Sanz-Garcia C, Ross CKC, Roychowdhury S, Bellar A, McMullen MR, Dasarathy J, Allende DS, Caballeria J, Sancho-Bru P, McClain CJ, Mitchell M, McCullough AJ, Radaeva S, Barton B, Szabo G, Dasarathy S, Nagy LE. (2021). Differential role of MLKL in alcohol-associated and non-alcohol-associated fatty liver diseases in mice and humans. (*Co-first author) JCI Insight. 22;6(4).
- Wu XQ, Nagy LE. (2020). MLKL contributes to Western diet-induced liver injury through inhibiting autophagy. Autophagy, 16(7):1351-1352.
- Wu XQ, Poulsen KL, Sanz-Garcia C, Huang E, McMullen MR, Roychowdhury S, Dasarathy S, Nagy LE. (2020). MLKL-dependent signaling regulates autophagic flux in a murine model of non-alcohol-related fatty liver disease. J Hepatol,S0168-8278(20)30185-9.
