Blunt Thoracic Aortic Injury
Original Date: 07/2025
Patients who suffer a blunt aortic injury typically present after deceleration-type injuries and with severe chest trauma. Blunt aortic injury is diagnosed by CT Chest with IV contrast.
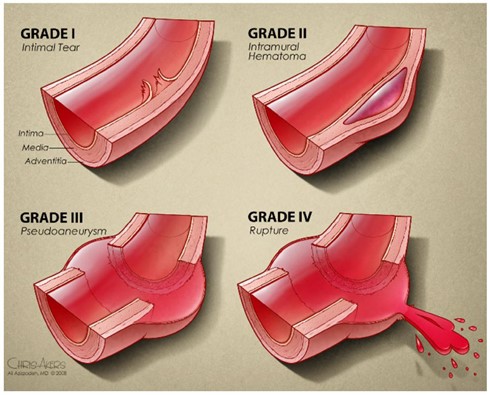
Injury Grading:
- Grade 1 – intimal tear
- Grade 2 – intra-mural hematoma
- Grade 3 – pseudoaneurysm
- Grade 4 – pseudoaneurysm with rupture
Initial Medical Management:
- Therapeutic targets are: SBP ≤120 mmHg and pulse ≤90 bpm.
- If SBP >120 mmHg or pulse >90 bpm, start esmolol 500 micrograms/kg bolus over 30 seconds.
- Start esmolol infusion at 50 micrograms/kg/min
- Titrate drip to achieve SBP target.
- Oral beta-blockers may be given in stable patients able to take pills by mouth.
Treatment:
- Grade 1 injuries are generally managed medically with repeat imaging as indicated.
- Grade 2 injuries may be managed medically or by TEVAR.
- Grade 3 injuries without high risk features should undergo TEVAR within 24 hours after admission.
- Grade 3 injuries with high risk features should undergo emergency TEVAR.
- High risk features:
- Aortic arch hematoma
- Ascending aortic, aortic arch, or great vessel involvement
- Mediastinal hematoma causing mass effect
- Posterior mediastinal hematoma >10 mm
- Lesion to normal aortic diameter >1.4
- Large left hemothorax
- High risk features:
- Grade 4 injuries should undergo emergency TEVAR.
Medical Management:
- Anti-platelet therapy:
- Given for all grade injuries and for medically and surgically treated patients as allowed by concomitant injuries and medical problems
- Dose: 81 mg per day.
- Non-operative management: continue until lesion resolves on imaging
- After TEVAR: continue for 30 days post operatively
- Blood pressure and heart rate targets:
- Non-operative management: transition esmolol drip to oral beta blockers to goal SBP <120 mmHg and pulse <90 bpm. Continue until lesion resolves on imaging.
- After TEVAR: no blood pressure or heart rate management required.