Jaw Surgery
Distraction Osteogenesis
Distraction osteogenesis (DO) has revolutionized craniofacial surgery. DO involves cutting bone and then slowly moving the cut ends of the bone. The gradual movement of the two cut pieces of bone results a new bone formation in the resulting gap. Distraction osteogenesis can be used in the lower jaw (mandible), the upper jaw (maxilla) and face (midface). There are a number of commercially available distraction devices. These devices may be placed beneath the skin or external to it. Distraction osteogenesis enables the surgeon to perform certain procedures which were not possible with conventional surgery.
Upper Jaw and Face Distraction Osteogenesis
Distraction osteogenesis has enabled the surgeon to move the upper jaw and face further and safer than with conventional surgery. An external rigid distraction device is the most commonly used distractor for upper jaw and face. The advantage of this device is that it is easy to apply and allows for adjustments during distraction. However, the device is bulky, uncomfortable, and not well accepted by most patients.
An internal distraction device is available in several different designs. The advantages of internal device are that it is better tolerated by patients and nearly invisible. The disadvantages of this device are that adjustments during distraction are not possible, and a separate surgical procedure is needed to remove the device.
The doctors at The University of Texas Health Science Center in Houston use both the internal and external device. They have developed two new internal distraction devices for use in the upper jaw and face. In addition, in order to help plan the distraction process, they have also developed a computer-assisted surgical simulation system. This involves taking a CT scan and simulating the surgery and the movement of the upper jaw and face.
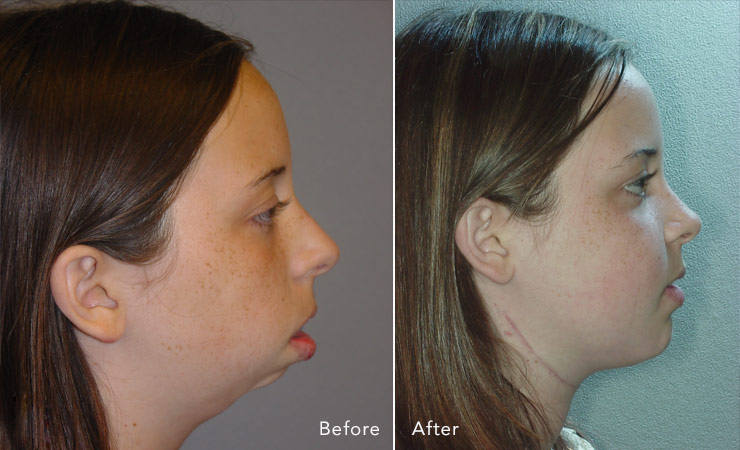
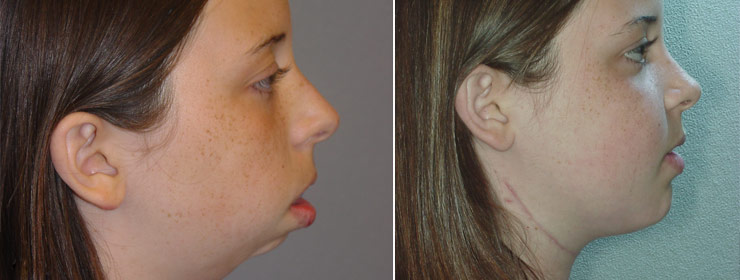
Lower Jaw
Distraction osteogenesis of the lower jaw is a very complex procedure. Most surgeons utilize an external device for distraction of the lower jaw, but there are also a few surgeons who use an internal device. The Texas Cleft and Craniofacial Team at The University of Texas Health Science Center use both internal and external distraction devices. The doctors have created a surgical planning simulation system to plan distraction in the low jaw. Distraction of the lower jaw is much more complex than distraction of the upper jaw and face. Planning in the lower jaw also involves taking a CT scan, and simulating surgery and distraction.
Neonate Distraction
Mandibular Distraction is a treatment of lengthening the lower jaw by stretching a healing fracture site. This is a technique to improve respiratory obstruction in patients with Pierre Robin Sequence. Pierre Robin Sequence is a condition in which the lower jaw is small, resulting in base of tongue obstruction of the airway. Patients often have cleft palate. In addition to respiratory difficulties, these children also have feeding difficulties. Children with feeding difficulties sometime require a gastrostomy tube. Traditional treatments have included positioning, supplemental oxygen, nasopharyngeal tubes, tongue-lip adhesion, and tracheostomy. While each may be indicated in certain situations, mandibular distraction provides a definitive result in a short period of time.