
Kuang-Lei Tsai, PhD
- Assistant Professor
- CPRIT Scholar, Cancer Prevention Research Institute of Texas
Areas of Interest
Research Interests
mediator, transcription, gene regulation, epigenetics, cancer, nucleosome, chromatin remodeling, long noncoding RNA (lncRNA), 3D genome architecture, structure, x-ray crystallography, Cryo-electron microscopy
Many human diseases are often caused by abnormal gene expression. In human cells, gene expression is tightly regulated by many large macromolecular complexes, such as coactivators, chromatin remodeling complexes, and long non-coding RNA molecules (lncRNAs). Studying their structures and molecular mechanisms is necessary for understanding how these complexes work and how gene regulation is controlled. Recent development in cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) has already made it possible to determine the structure of the macromolecular complex at near-atomic resolution. We combine the advanced cryo-EM techniques with various biochemical and biophysical approaches to explore the structures and functions of macromolecular assemblies involved in gene regulation. Currently, we are especially interested in these two directions:
-
- Structural and functional studies of the eukaryotic transcription complexes.
The human 1.5 MDa transcriptional Mediator complex, consisting of 25 core Mediator proteins and a dissociable CDK8 kinase module, plays an essential role in transcriptional regulation by conveying regulatory signals to the RNA polymerase II (Pol II) transcription machinery. While the molecular mechanism by which Mediator regulates transcription has not been entirely elucidated; its dysfunction and dysregulation have been extensively linked to a variety of human diseases, including cancer. Recently, we successfully determined the core Mediator structure at near-atomic resolution (Figure 1), revealing the molecular interactions between core Mediator and Pol II during transcription initiation (Published in Cell 2014 and Nature 2017). Our near-term goals are to 1) explore the molecular mechanism underlying Mediator regulation by lncRNA and 2) identify new lncRNAs potentially linked to diseases through interactions with Mediator. - Macromolecular complexes involved in regulation of 3D genome architecture.
In the cells, the structure of the 3D genome influences gene regulation, evolution, and cell fate decisions. How chromatin is organized within the nucleus and how genome architecture is regulated and maintained are important emerging biological questions. To regulate genome architecture, numerous protein complexes are involved in this process. We will use various structural and molecular approaches to study the structures and molecular mechanisms of the complexes involved in the regulation of genome architecture.
- Structural and functional studies of the eukaryotic transcription complexes.
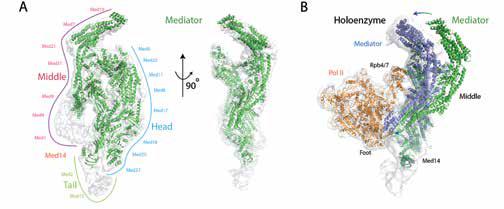
Figure 1. Transcriptional Mediator and its complex with RNA polymerase II (Pol II). (A) Structure of the core Mediator. (B) Structure of Mediator and Pol II complex. Conformational change of Mediator is required for its interaction with Pol II.
Selected Publications
Tsai KL, Yu X, Gopalan S, Chao TC, Zhang Y, Florens L, Washburn MP, Murakami K, Conaway RC, Conaway JW, Asturias FJ. 2017. Mediator structure and rearrangements required for holoenzyme Formation. Nature. 544:196-203.
Murakami K, Tsai KL, Kalisman N, Bushnell DA, Asturias FJ, Kornberg RD. 2015. Structure of an RNA polymerase II pre-initiation complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 112:13543-13548.
Tsai KL, Sato S, Tomomori-Sato C, Conaway RC, Conaway JW and Asturias FJ. 2014. Subunit architecture and functional modular rearrangements of the transcriptional Mediator complex. Cell. 157: 1430-1444.
Tsai KL, Sato S, Tomomori-Sato C, Conaway RC, Conaway JW and Asturias FJ. 2013. A conserved Mediator–CDK8 kinase module association regulates Mediator– RNA polymerase II interaction. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 20: 611-9.
Education and Training
Undergraduate
National Cheng Kung University
PhD
National Tsing-Hua University
Postdoctoral Fellow
The Scripps Research Institute, San Diego
Graduate Program Affiliation
Molecular and Translational Biology
Cancer Biology