Overview
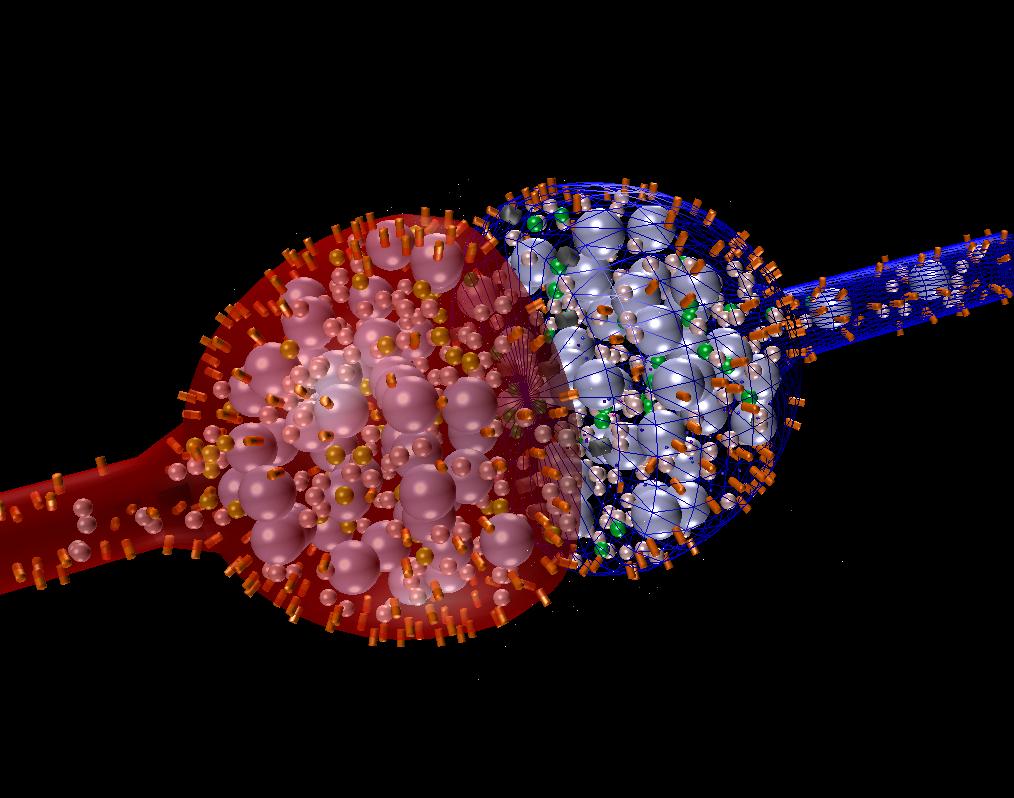
A synaptic transmission example with vesicle release, diffusion across a cleft, binding to NMDA receptors, and calcium influx binding to calmodulin and CaMKII.
The Cellular Dynamic Simulator (CDS) was designed to simulate diffusion and chemical reactions within crowded molecular environments. CDS is based on an event driven algorithm that allows precise calculation of the timing of collisions, reactions and other events for each individual molecule in the environment. Generic mesh based compartments allow the creation / importation of very simple or detailed cellular structures that exist in a 3D environment. Multiple levels of compartments and static obstacles can be used to create a dense environment to mimic cellular boundaries and the intracellular space. Diffusing molecules move in a Brownian fashion by generating a random displacement at specified time intervals. This novel algorithm can address how volume exclusion and molecular crowding impact signaling cascades in small sub-cellular compartments such as dendritic spines.
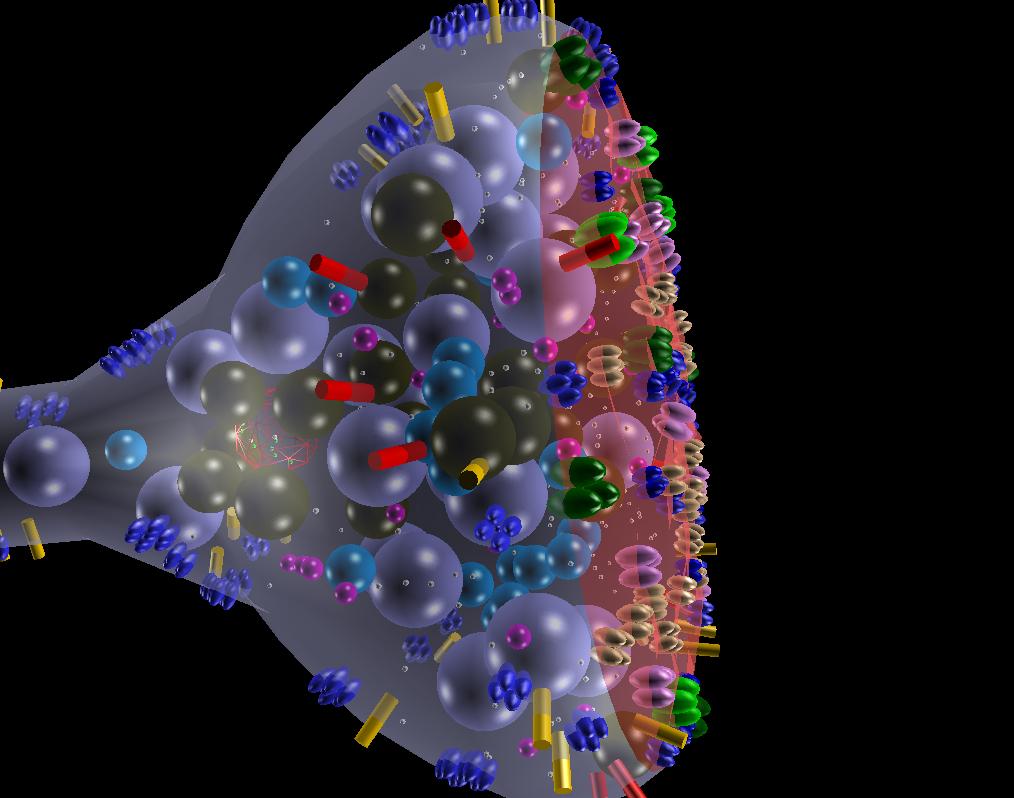
Membranes can be densely populated with multiple subunit receptors that can be static as well as diffusing along the membrane.
With the CDS, we can simulate simple enzyme reactions, aggregation, channel transport, as well as highly complicated chemical reaction networks of both freely diffusing and membrane-bound multi-protein complexes. Components of the CDS are generally defined such that the simulator can be applied to a wide range of environments in terms of scale and level of detail.
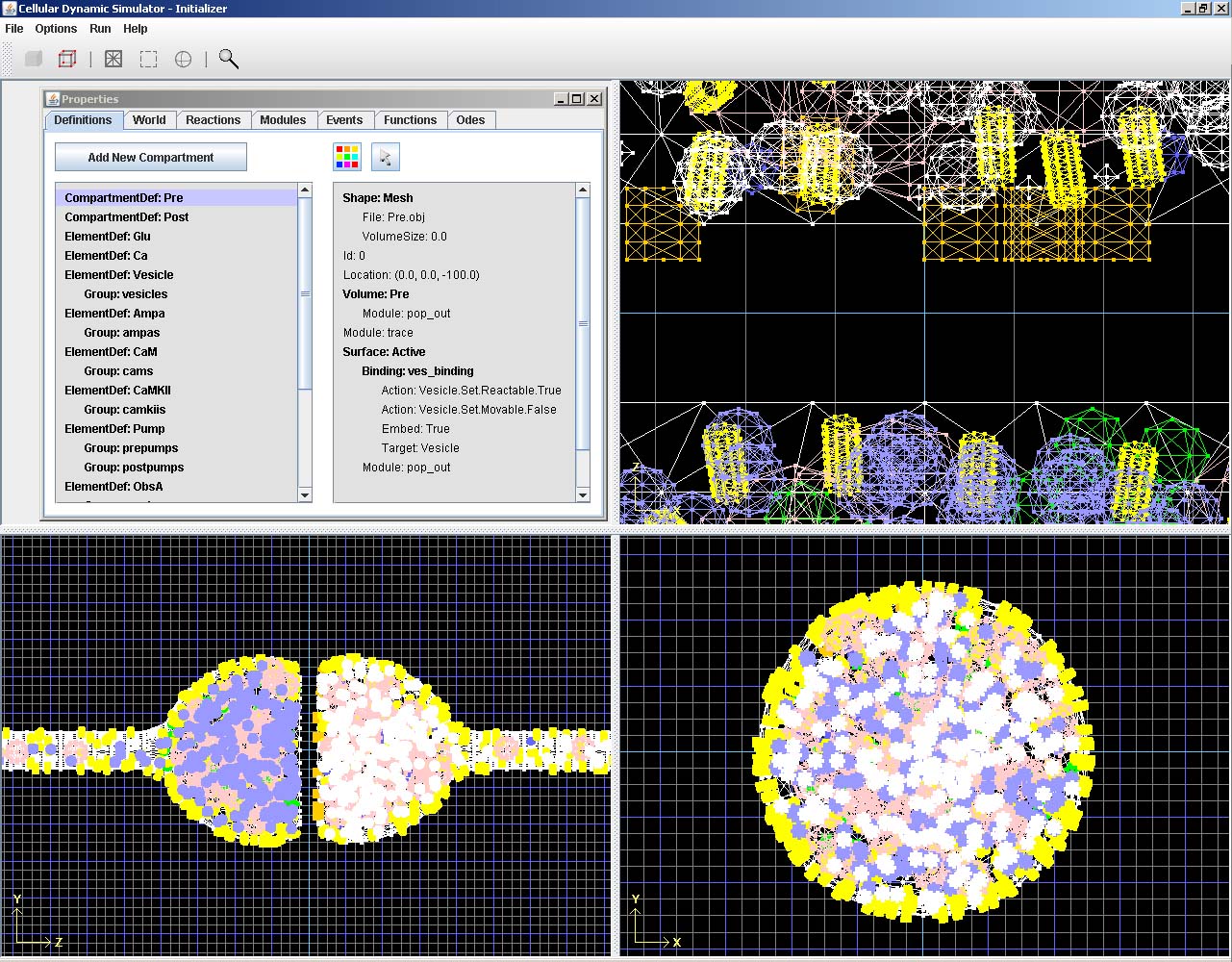
A separate initialization tool allows the user to create the simulation environment to be loaded by the simulator. It can be extremely time-consuming to create even simple environments manually, so the Initializer allows for automatic creation of meshes and distribution of molecules in volumes and along membranes while preserving volume exclusion. Meshes can be easily created based upon several prefabricated designs. Once a mesh is created or imported, the Initializer allows for a variety of mesh manipulation tools to create specific geometry without having to rely on third-party 3D editing software.
A third software tool included with CDS is 3D visualization software that can take simulator output and render it as a live, continuous animation. A variety of playback controls allow the user to view the simulation at any speed, movies can be rendered and high-resolution screenshots can be taken.