An Investigation of Th-1 Dendritic Cell Immunotherapy in Combination with Standard Chemoradiation for Adjuvant Treatment of Adult Glioblastoma

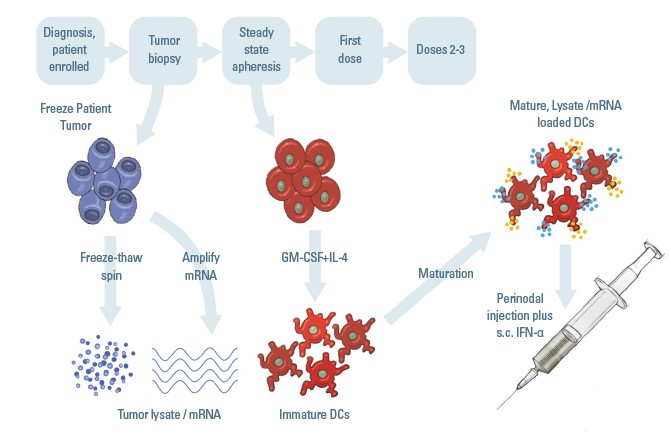
In this non-randomized, first-in-human pilot trial, researchers at UTHealth Houston aim to evaluate the safety and feasibility of delivering a dendritic cell vaccine to adult patients diagnosed with glioblastoma (GBM). The study is led at Memorial Hermann-Texas Medical Center by co-investigators Yoshua Esquenazi, MD, assistant professor and director of surgical neuro-oncology at UTHealth Houston Neurosciences in the Vivian L. Smith Department of Neurosurgery, and Sigmund H. Hsu, MD, an assistant professor also in neurosurgery.
Director of Surgical Neuro-oncology Dr. Yoshua
Esquenazi’s research studies the use of a novel dendritic cell vaccine for glioblastoma.
“Our glioblastoma patients desperately need effective adjuvant therapies. Standard-of-care therapies are rarely successful in preventing recurrence among GBM patients, and death rates are high among patients with the disease,” Esquenazi says. “In this Phase I clinical trial we’re assessing the safety of a novel personalized dendritic cell vaccine administered shortly after patients complete standard-of-care chemotherapy and radiation.”
The investigators have successfully completed treatment in 16 participants in Houston and at Cooper University Hospital in Camden, New Jersey. To be eligible, patients must have undergone tumor resection and chemoradiation and have an established neuropathological diagnosis of GBM. The study involves three steps of dose escalation in a 3+3 algorithm with rigorous mandatory safety monitoring. “Our goal is to boost the immune system to eradicate cancer by generating robust Th-1 type immunity and generating lasting immunological memory to work against the tumor cells,” Esquenazi says.
The preliminary results of this trial indicated that the vaccination is safe, can be effectively integrated into existing standards of care, and is potentially efficacious in a challenging patient population. For more information, visit clinicaltrials.gov and search the identifier NCT04552886.
In This Section:
Features:
- True to Our Values
- The Heart-Brain Program: A Closed-Loop Continuum of Care to Patients with PFO-Associated Stroke
- Multidisciplinary Programs Provide Convenience and a Broader View of Health to Physicians and Patients
Patient Stories:
- Alabama Woman Finally Gets a Sleep Disorder Diagnosis Through Telehealth
- Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) for severe back pain
- Finally Getting a Good Night’s Sleep with remedē®
Research & Trials:
- Sensitizing Tumors to Radiation Therapy Using Gold Nanoparticles
- An Investigation: Th-1 Dendritic Cell Immunotherapy in Combination with Standard Chemoradiation for Adjuvant Treatment of Adult Glioblastoma
- Advances in the Diagnosis and Management of Cluster Headache
- AI-Powered Algorithms May Help Detect Unruptured Brain Aneurysms
Accolades & News:
- Department of Neurosurgery Ranks 4th in NIH Funding Among US Clinical Science Departments
- McCullough Wins Stroke Association Lecture Award
- UTMOVE Receives Distinguished Edmond J. Safra Fellowship in Movement Disorders
- Schiess Awarded UTHealth Houston President’s Scholar Award
- Burish Co-Chairs the AHS Scientific Program Committee
- Furr Stimming Named HSG Outstanding Investigator
- Lo Receives UT System STARs Award
- Burish Assumes Responsibility for Neurology Residency Training for Headache Medicine
- Morcos Named Chair of Neurosurgery