Audiogram
This section is for professionals who have testing equipment available. A more detailed explanation of how to perform and interpret these tests can be found in any standard Audiology or ENT (Ears, Nose and Throat) textbook. There are two types of basic tests that will normally be done in these settings. One of the tests is an audiogram and the other is a Tympanogram. The audiogram tests for hearing loss while the Tympanogram test for compliance (movement) of the ear drum.
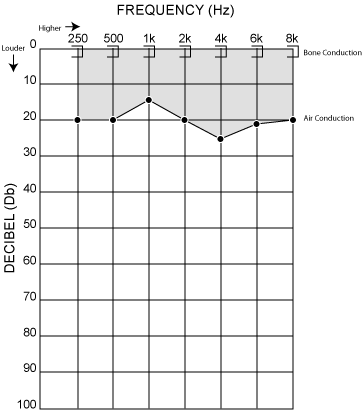
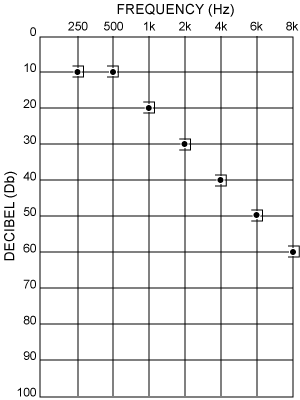
AUDIOGRAM
Hearing losses can be broken down into three basic types:
- Conductive Hearing Loss
- Neurosensory Hearing Loss
- Mixed Hearing Loss
CONDUCTIVE HEARING LOSS
This type of hearing loss is caused by a decrease in conduction of sound into the ear. Some examples of aliments that would cause a decrease of conduction are: wax clogging the ear, or a hole in the ear drum. Each of these types of problems can be treated and corrected.TESTING RANGES
Normal range is between 0-20 Db
Speech range is 500-2000 Hz
Below 35 Db’s, hearing aids are recommended
NEUROSENSORY HEARING LOSS
This type of hearing loss is secondary to nerve damage. Some examples of disorders that would cause neurosensory hearing loss are: noise exposure, familial (inherited) hearing loss, damage from infection or decreased hearing with old age. For all intent and purpose nerve damage cannot be corrected.
MIXED HEARING LOSS
This type of hearing loss is a combination of Neurosensory Hearing Loss and Conductive Hearing Loss.